Blog
News, updates, finds, stories, and tidbits from staff and community members at KAHEA. Got something to share? Email us at: kahea-alliance@hawaii.rr.com.
NWHI Marine Monument Hearings on Oahu TV
From our buddy Oren, who helped us get this public hearing documented and on air:
The video taping of the Honolulu hearing on the Draft Management Plan for The Papahanaumokuakea Marine Monument in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands held in Honolulu on June 24th will be aired on ‘Olelo Community Television on ch. 52 as well as on its internet website olelo.net–which simultaneously streams ch. 52.
7/3/08 Thu 1:00 pm
7/10/08 Wed Midnight
7/17/08 Wed Midnight
7/24/08 Thu 1:00 pm
In a few days we maybe able to get it on the internet for anyone to watch at any time.
I’d like to thank especially Bill Sager, John Isagawa, Dave Gonzales, Rob Kinslow and the peoples’ at ‘Olelo Community Television —with a lot of their efforts—-, all of whom, who helped to tape this thing together.
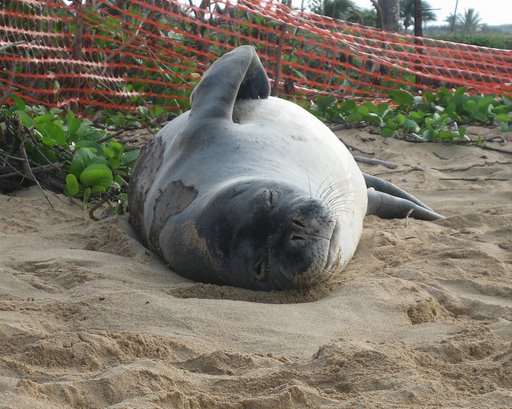
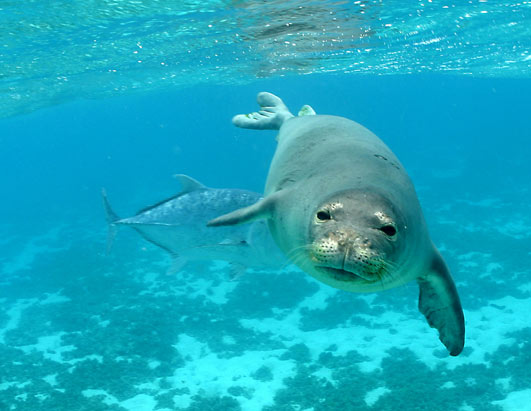
WANTED: Critical Habitat for Monk Seal

KAHEA, along with the Center for Biological Diversity and the Ocean Conservancy, filed a formal petition yesterday, seeking to have beaches and surrounding waters on the main Hawaiian islands designated as critical habitat for Hawaiian monk seals under the Endangered Species Act.
Under the Endangered Species Act, critical habitat identifies geographic areas that contain features essential for the conservation of a threatened or endangered species and may require special management considerations.
Recent studies have shown that species with critical habitat are twice as likely to be recovering as species without it. Currently, the species has critical habitat designated only on the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands.
The Hawaiian monk seal is one of the most endangered marine mammals in the world. Since the 1950s its population has dropped to about 1,300 animals and is continuing to decline. Scientists estimate populations will likely drop below 1,000 seals within a few years.
Monk seals in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands are dying of starvation, emaciated and weak, scientists have found. Pups have only about a one-in-five chance of surviving to adulthood. Other threats include drowning in abandoned fishing gear, shark predation, and disease.
Hawaiian monk seals are increasingly populating the main islands, where they are giving birth to healthy pups. For the past decade, the number of Hawaiian monk seal births has increased each year on the main islands, and the population of seals is growing steadily; the seals are in better condition than those in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. This indicates more food availability and a better chance of survival.
Global warming is also a threat to the survival of Hawaiian monk seals. Already, the conservation groups warn, important pupping beaches have been lost due to sea-level rise and erosion, and the northwestern islands will eventually disappear under predicted levels of sea-level rise since they are elevated only a few meters above sea level. The higher-elevation main islands are less vulnerable to sea-level rise.
Hawaiian monk seals are one of three species of monk seals. The Mediterranean monk seal is also critically endangered, while the Caribbean monk seal, which has not been seen in half a century, was declared extinct in June.
The Endangered Species Act requires that the government respond to this petition within 90 days.
Say NY Times and Star Bulletin: Navy should comply with Environmental Laws
(graphic from abcnews.com)
The Supreme Court has taken up the question of whether the Bush Administration can exempt the Navy from laws protecting marine mammals from sonar, and media is chiming in. Both the New York Times and Star Bulletin have come out recently in favor of upholding environmental law when it comes to Navy training exercises.
From Op-Ed in today’s New York Times:
Environmentalists have long claimed that the Navy’s use of sonar for training exercises unduly threatens whales, dolphins and other acoustically sensitive marine creatures. The Navy has adopted some procedures to mitigate the risk but has resisted stronger protections ordered by two federal courts. The Supreme Court has now agreed to address the issue.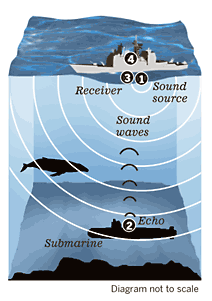
The justices will not try to determine the extent of harm but rather the balance of power between the executive branch and the courts in resolving such issues. In an effort to sidestep the courts, the Bush administration invoked national security to exempt the Navy from strict adherence to the two federal environmental laws that underlay the court decisions. The top court will now have to decide whether the military and the White House should be granted great deference when they declare that national security trumps environmental protection or whether the courts have a role in second-guessing military judgments and claims of fact.
The case at hand was filed by the Natural Resources Defense Council and other conservation groups to rein in Navy training exercises that use sonar to search for submarines off the coast of Southern California. The Navy says that its exercises pose little threat to marine life and that the training is vital to national security.
A federal district judge and a federal appeals court in California, after careful reviews of the facts, have found that the Navy’s arguments are largely hollow. Although the Navy likes to boast that there has never been a documented case of a whale death in 40 years of training, that may be mostly because no one has looked very hard. The Navy itself estimates that the current series of drills, conducted over two years, might permanently injure hundreds of whales and significantly disrupt the behavior of some 170,000 marine mammals.
No one has questioned that sonar training is vital to national security, and the federal courts have not tried to ban the training. They have simply tried to impose tough measures to minimize damage. The Navy objected to two proposed restrictions in particular — that it shut off its sonar when marine mammals are detected within 2,200 yards and power down its sonar under sea conditions that carry sound farther than normal.
High-ranking officers said these restrictions would cripple the Navy’s ability to train and certify strike groups as ready for combat. The appeals court, mining the Navy’s own reports of previous exercises, disagreed. It said the Navy, following earlier procedures, had already been shutting down sonars with little impact on training or certification.
It seems telling that the Navy has accepted the 2,200-yard safety zone for other sonar exercises. NATO requires the same zone, and the Australian Navy mandates a shutdown if a marine mammal is detected within 4,000 yards.
The federal courts have played a valuable role in deflating exaggerated claims of national security. Let us hope that the Supreme Court backs them up.
And, from our own Honolulu Star-Bulletin:
The Navy’s application for a new permit for sonar training exercises in Hawaii waters could be the last time it will need to go through the process, depending on a ruling from the U.S. Supreme Court.
Should the court agree with the Bush administration’s assertion that it has the authority to override laws that protect the environment and marine mammals, the Navy would no longer be required to seek the permits designed to minimize harm to ocean species.
The court is not expected to focus on a continuing dispute between the Navy and environmental organizations about the level of injury sonar causes to marine mammals.
Instead, justices will decide whether the administration, with the support of the military, can set aside enforcement of well-established law. The administration argues that protective conditions put in place by federal courts jeopardize “the Navy’s ability to train sailors and marines for wartime deployment.”
The claim is belied by the fact that the Navy has been able to conduct training while mitigating harm.
The case involves naval exercises off the Southern California cast in which a federal judge restricted mid-frequency sonar use and required it to be shut down when a marine mammal is sighted within 6,000 feet. In a similar ruling in Hawaii, federal Judge David Ezra established several guidelines, putting the range at 5,000 feet. The different requirements have frustrated the Navy, but they are due to variations in coastal waters and marine mammal populations.
While the California case was proceeding through the appeals court, President Bush exempted the Navy from the Coastal Zone Management Act. At the same time, an executive branch agency, the Council on Environmental Quality, granted an exemption of the National Environmental Policy Act, claiming an emergency situation. The Defense Department has previously claimed an exception for “military readiness activity,” as allowed under the Marine Mammal Protection Act.
Through these laws, environmental groups have been successful in establishing restrictions, showing evidence that sonar soundings have injured or led to the deaths of whales. Navy studies have shown probable harm, disturbance or death to 175,000 marine mammals. The Navy also says only 37 whales have died from sonar since 1996, but that doesn’t mean that other haven’t been killed without their carcasses being found.
(Photo: 2006 dolphin stranding, Mozambique.)
The administration’s crafty argument, however, is aimed at defining the scope of executive authority, which might be a gamble because the court has not been sympathetic to Bush’s attempts to stretch presidential power.
A ruling will have implications in Hawaii, where the Navy’s permit for sonar exercises will expire in January. Until the court’s decision in its next term, the public has an opportunity to weigh in with the argument that training can be conducted effectively while reducing the risk of harm to animals in the sea.
Where's the public in this "public process"?
From Evan, law school student and Legal Fellow from the Center for Excellence in Native Hawaiian Law working on staff with KAHEA this summer:
Was thrown into the deep waters of the 1,200 page Papahanaumokuakea Draft Monument Management Plan for the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands this summer. It’s given me a unique opportunity to observe the workings of this “public” process. I’ve worked with experts in reviewing the plan, and attended several of the public hearings set up by the State/Federal Co-Trustee agencies. My observation: It is a recipe for disaster to take two years of closed door processes, package it into 4 very thick volumes and then expect the public at large to comment in any detail about what the plan entails. 
(This is what 700 pages of the 1,200 page plan looks like. Erm, fun.)
I first attended the hearing at the Department of the Interior in Washington D.C. (the only hearing held outside our lovely archipelago). I was quickly made aware of the fact that I would be the only person offering public testimony. So much for the public in this public hearing.
After giving an impassioned 20 minute explanation of KAHEAʻs overarching concerns, I was flooded with a steady stream of “How do you do’s?” and “Can we get a copy of your testimony?” from interested national NGO’s and congressional staffers. I was glad for the opportunity to get the word out on our key concerns, despite the dismal showing of public engagement.
The next chance I had to attend was the final night of the Federal/State Co-Trustee Island Summer Hearings Tour 2008. From all accounts, the crowd of about 60 at the Japanese Cultural Center in Moilili was by far the largest of any of the meetings. The format was a little different from D.C. and to be honest, quite unlike anything I had ever witnessed before. After a formal introduction to the Monument (same as D.C.), was an open discussion with Monument staff who were broken into 6 tables that synchronized with 6 priority management needs from the plan. It had an element of “spoon-feeding” to it, and considering that many had come to supply public testimony, made things run a little later than they may have otherwise. Nonetheless, I found this segue to be a nice opportunity to bring some of my major gripes with the plan directly to the folks who had put it together.
Over the course of this experience, I have been amazed at the bizarre nature of this top-down “public” process.
When asked: “Why was the citizen’s advisory council removed from the plan?”
A rep responded: “Actually, we do want one. We left it out because we wanted to see what the public would come up with during the review period.”
I’d suggest that a proper, engaged public process wouldn’t have waited until the review period to see what the “the public would come up with.” It all reminded me of the hide the ball game my law professors sometimes like to play. Except this is not law school. Why intentionally leave something as important as public oversight and advisory committees out of the plan, on purpose? Something as important as the Monument surely deserves better!
All told, the nine public meetings yielded about 250 total attendees and 70 testifiers. Not exactly up to par with the 100,000+ comments that helped create the Monument. Essentially, there was very little public at in these public meetings.
It is the job of the government managers to engage the public in this process–to bring the place and the process to the people. The length of time since the Co-Trustees have seen daylight, coupled with the sheer magnitude of the plan are likely culprits for this erosion of public engagement. I simply cannot accept that after previous outpourings of energy, suddenly nobody cares enough about this place to speak out. Another likely reality involves the seventy five day open period for submitting comments, which is rapidly coming to a close on July 8th. Compared to the two years it took countless full time staff to develop the plan, 75 days is simply too short a time to garner the effective and real public involvement needed to protect this special place.
This is one of the truly intact Hawaiian reef ecosystems left on earth–precious cultural and natural heritage that deserves our attention and voices. You can learn more about problems with the current plan, and how to ask for a better process and more time to get the “public” involved at: www.kahea.org.
enforcement means everybody, folks.
From Miwa:
On June 13, the Hawai`i Board of Land and Natural Resources quietly denied the permit of HIMB disease researcher Greta Aeby, in the closing chapter of a historic enforcement action for the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Aeby was reported in 2006 by fellow researchers to be transporting potentially diseased coral shipboard in an open-flow system–a clear violation of her research permit.
After initially contesting the violation, she and HIMB finally accepted the enforcement action earlier this year. (But only after third-party legal intervention by us at KAHEA!) She remains under investigation for other violations related to illegal disease cultivation and importation.
We have taken some heat for standing up and urging the full enforcement of the law for this HIMB researcher. Do we hate HIMB? Do we hate researchers? Absolutely not. There are plenty of good people who work at HIMB, many of whom are our friends.
What we ARE saying is that no matter who you are, the rules apply. HIMB researchers, commercial and recreational fishers–all the same. The protective rules are in place for good reason, rules for which many people fought incredibly hard. Through many years, and sometimes at great personal expense, they fought to protect this place as an intact natural and cultural legacy for future generations. This is about responsibility and it is about respect. Responsible research is about respect for the resource and respect for the people to whom the resource ultimately belongs.
Thanks to the participation of over 100,000 members of the public, the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands are today protected as the largest no-take marine reserve on the planet. Permits are required to access the area, and research permits in particular, are considered a privilege for those researchers who are contributing directly to conservation of the area and can conduct their activities responsibly–with little to no impact. This is because our policies and rules in Hawai`i recognize that irresponsibly conducted research poses serious risks and can cause serious harms.
We commend the BLNR for upholding the rules in place to protect the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Through strong rules and strong enforcement, we can continue to keep this place as a true pu`uohonua. Forever.
We live in the endangered species capitol of the planet, islands impacted heavily by the onslaught of invasive species and the impacts of climate change on our Hawaiian reefs. In the face of all this, we believe that for this one, last intact and pristine Hawaiian place, we can act together to do the right thing.
conservation plan = more impacts? we don't get it.
A short video we put together on the new draft of a 15-year plan for the future of the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands.* We’ve read all 1,200 pages of it, and reviewed it with experts everywhere from Sierra Club to Environmental Defense. Our conclusion? We can do much, much better.
Now, we’re seeking signatures on a petition asking for a better, stronger Plan for this fragile wahi pana.
The current draft is a plan for conservation which, inexplicably, actually expands the footprint of human activity in this pristine and uniquely Hawaiian coral reef ecosystem.
In the largest no-take marine reserve on the planet, this draft of the Federal/State plan is proposing the construction of a “small municipality” on Midway, new cruise ships, more tourists, increases in extractive research, new risks of invasive species introductions, exemptions for fishing, and opening of the area to bioprospecting. An expansion of military activities–including sonar, ballistic missile interceptions, and chemical warfare simulations–would be allowed to go forward with no mitigations. The plan also disbands the existing citizen advisory council, which is pretty much the only opportunity for members of the public (non-government scientists, advocates, cultural practitioners, and resource experts) to participate in decision-making. Yeesh.
Over 100,000 people from all over the world helped establish the Papahanaumokuakea National Marine Monument and the Hawaii State NWHI Refuge–perhaps the most visionary legal marine area protections in history. We need to ask government managers for a plan which upholds these strong protections. We should be working towards full conservation, NOT creating and formalizing exceptions to the rules. That’s our position, anyway.
If you agree, please take a few seconds to add your name to the petition. This last intact, endangered and uniquely Hawaiian coral reef ecosystem deserves a plan for its FULL conservation. Unless we show broad public support, protections we fought so hard for will be paper, not practice.
*The hearings mentioned in the video are over, but there is still one week left to make your voice heard. More information at www.kahea.org. Deadline is July 8, 2008.
Federal Court Issues Injuctions, Requires Navy to Do More to Protect Hawaii's Marine Mammals from Harmful Sonar
Hawai‘i federal district Judge David A. Ezra today found that the Navy is violating federal law and enjoined it from carrying out its Undersea Warfare Exercises in Hawai’i’s waters without adhering to additional mitigation measures to protect marine mammals. The Navy is also required to take a hard look at the impacts of its high-intensity, mid-frequency active (MFA) sonar by preparing an Environmental Impact Statement.
Earthjustice, on behalf of Ocean Mammal Institute, Animal Welfare Institute, KAHEA: The Hawaiian-Environmental Alliance, the Center for Biological Diversity, and Surfrider Foundation’s Kaua’i Chapter, sued the Navy last May. Judge Ezra issued a preliminary injunction after finding the Navy was violating the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and the Coastal Zone Management Act (CZMA), and was likely to cause harm if allowed to proceed without greater protections.
He noted the Navy’s harm threshold—173 decibels (dB)—contradicts the best available science, and “cast into serious doubt the Navy’s assertion that, despite over 60,000 potential exposures to MFA sonar, marine mammals will not be jeopardized.” The Court said further the Navy had failed to analyze reasonable alternatives to conducting its exercises in the manner it proposed, failed to notify and involve the public as required by law, and failed to take into account the potential for serious harm from an exceptionally controversial activity.
Learn more about the lawsuit and the impacts of high-intensity mid-frequency (MFA) sonar on Hawaii’s marine mammals.














